Docker + Docker Compose
YouTube Video
Commands
Docker
docker pull <image>: Pull Image from Docker Hubdocker create <image>: Create a container from an Imagedocker start <container_name/container_id>: Start a containerdocker stop <container_name/container_id>: Stop a containerdocker kill <container_name/container_id>: Kill the entrypoint process of the containerdocker rm <container_name/container_id>: Remove a containerdocker ps: Get all running containersdocker ps -a: Get all containersdocker stop $(docker ps -a -q): Stop all containersdocker rm $(docker ps -a -q): Remove all containersdocker image rm $(docker image ls -q): Remove all imagesdocker run --name <container_name> -p <host_port>:<container_port> <image>: Pull, create, start and run a containerdocker run -d <image>: Run in detached modedocker run -e <key>=<value> <image>: Run with environment variabledocker run -it <image> <command>: Run a container and overwrite the default commanddocker run -it --entrypoint <entrypoint_command> <image>: Run a container and overwrite the default entrypointdocker inspect <container_name>: Get details about the containerdocker exec -it <image_name> <command>: Execute a command in a running container with interactive modedocker -v <volume_name>:<path_in_container> <image>: Bind path in the container to a Docker volumedocker -v <path_in_host>:<path_in_container> <image>: Bind path in the container to another path in the hostdocker volume ls: List all volumesdocker volume create <volume_name>: Create a Docker volumedocker network create <network_name>: Create a user-defined networkdocker run --network=<network_name> <image>: Run a docker container in a certain networkdocker run --link=<container> <image>: Run a docker container and link network it with another container (legacy)docker build <path>: Build docker imagedocker build --tag <image_name> <path>: Build docker image with a tagdocker build --platform linux/amd64 <path>: Build for a specific target platform. This is used when building on M1 Macbook but target is linux.docker build - < <custom_path>: Build docker image when the name is notDockerfiledocker tag <image_name> <company>/<new_image_name>:<version>: Add a Docker Repository tag to an image. It can be also used for adding more tagsdocker login: Log into a Docker Repositorydocker push <company>/<new_image_name>:<version>: Push to a Docker repository, ex: DockerHubdocker commit <container_name/container_id> <image>: Create an image from a running containerdocker logs -f --tail <lines_count> <container_name>: Print number of lines of the container logs and keep streamingdocker stats: Show live streaming of the containers' resource usage
Docker Compose
docker compose build: Build services of the docker composedocker compose build <service>: Build a service of the docker composedocker compose create: create servicesdocker compose start: start servicesdocker compose run: Run a command in a servicesdocker compose restart: Restart servicesdocker compose restart <service>: Restart a servicedocker compose pause: Pause servicesdocker compose unpause: Unpause servicesdocker compose stop: Stop servicesdocker compose rm: Remove stopped containersdocker compose up: Create and start containersdocker compose pull: Pull all services' images. It's good when updating services imagesdocker compose up -d: Create and start containers in detached modedocker compose up -d <service>: Create and start containers in detached mode for a certain servicedocker compose up --scale <service>=<count>: Create and start containers and scale the number of a servicedocker compose down: Stop and remove containersdocker compose logs -f --tail <lines_count>: Print the logs for all services.-fmeans follow and--tailis the number of lines.docker compose logs -f --tail <lines_count> <service>: Print the logs for a certain services
DockerFile
FROM <image>: Based imageFROM <image> as <stage>: Based image, also assign name to be used for multi-stage image buildingRUN <command>: Runs a certain command inside the imageExpose <port>/<protocol>: Used for documentation purposes to available portsCOPY <source> <destination>: Copys file from host to imageCOPY --from=<stage> <source> <destination>: Copys file from host to image. Cross stage copy.ADD <source> <destination>: Similar toCOPYbut can also download and extract tar filesENV <key>=<value>: Define an environment variablesUSER <user>:<group>: Used to define a user to run the commandsWORKDIR <destination>: Set working directory to avoid manycdCMD <command> <param1> ...orCMD ["<command>", "<param1>"]: The default command to run for the containerENTRYPOINT <command> <param1> ...orENTRYPOINT ["<command>", "<param1>"]: The required command to run for the container.
Docker Compose File
services: Array of services to startimage: Docker image namebuild: Path to a Dockerfileport: Array of exposed portsenvironment: Array of environment variablesvolumes: mapping of volumesnetworks: Define used networkrestart: Restart policy for the container.no,on-failure,always,unless-stopped
networks: Defines available networks
Questions?
ADDvsCOPY?They both have similar functionality but
ADDcan also extract tar file and also download from the networkCMDvsENTRYPOINT?They both execute commands. Use
CMDwhen you want the user of your image to have the flexibility to run whichever executable they choose when starting the container. UseENTRYPOINTwhen you want the container to behave exclusively as if it were the executable it's wrapping.
We can combine both of them and use ENTRYPOINT when we need a command to always run when the container starts and CMD to pass the parameters. We can then allow our users to overwrite the paramters when using docker run.
exposevsport?exposeis used for documentation purposes to available ports. It does not expose the port to the host machine.portis used to map the port from the host machine to the container.
Diagrams
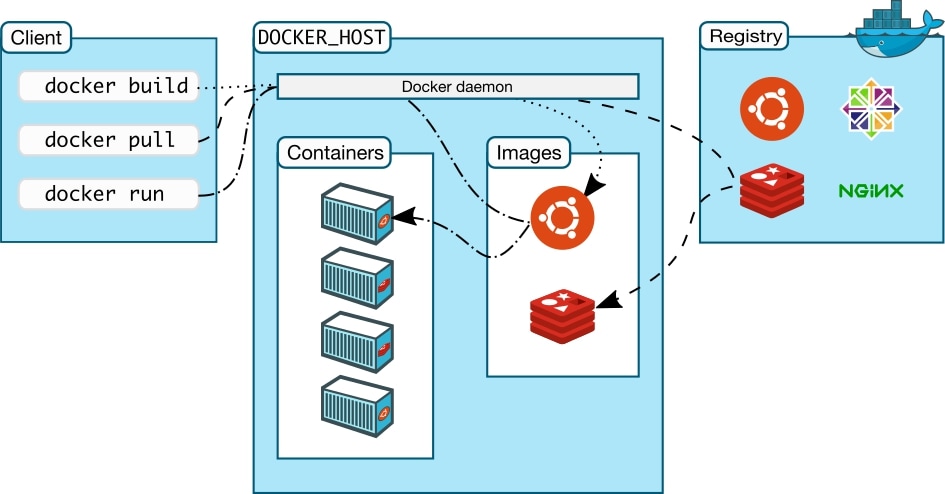 Source: Docker Docs
Source: Docker Docs
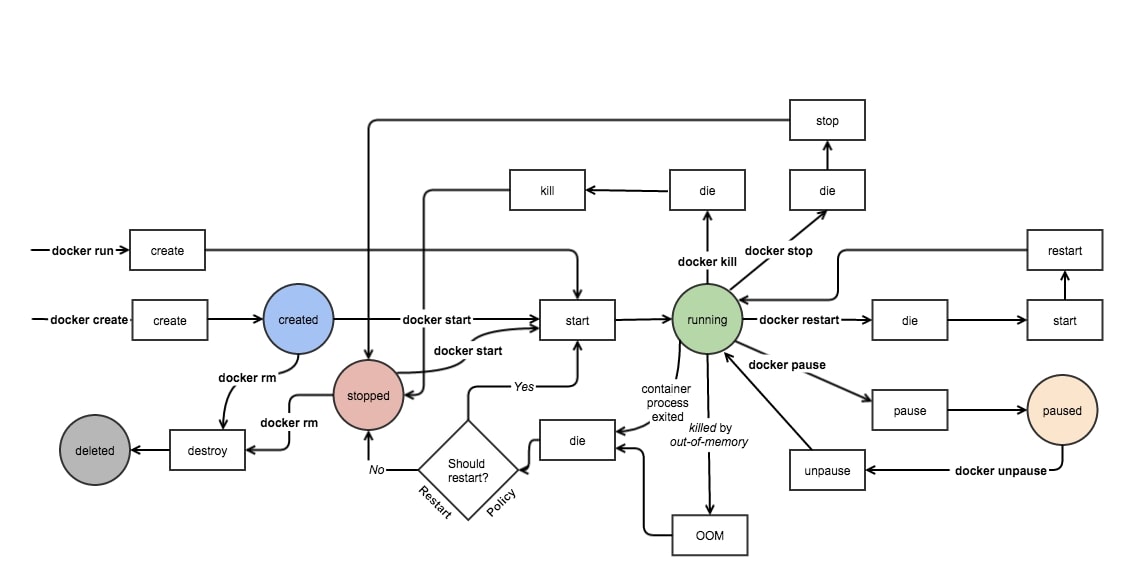 Source: Docker Internals
Source: Docker Internals
Interesting Docker Images
jwilder/docker-gen- Generate files from docker container meta-datajwilder/nginx-proxy- Automated Nginx reverse proxy for docker containers. It has both nginx and docker-gen. It also can be pulled asnginxproxy/nginx-proxybut they are essentially the same thing.nginxproxy/acme-companion- Automated ACME SSL certificate generator for nginx-proxy container.ghcr.io/letsencrypt/pebble- An ACME test server, useful to test against a Let's Encrypt server.